Chinese Odyssey 64
Saw my favorite Guanyin
and we stopped for a soda
Remembered Xuanzang
at the Wild Goose Pagoda
Rode bikes on a wall
which encircled Xi An
Inside the Great Mosque
we could hear the Qur’an.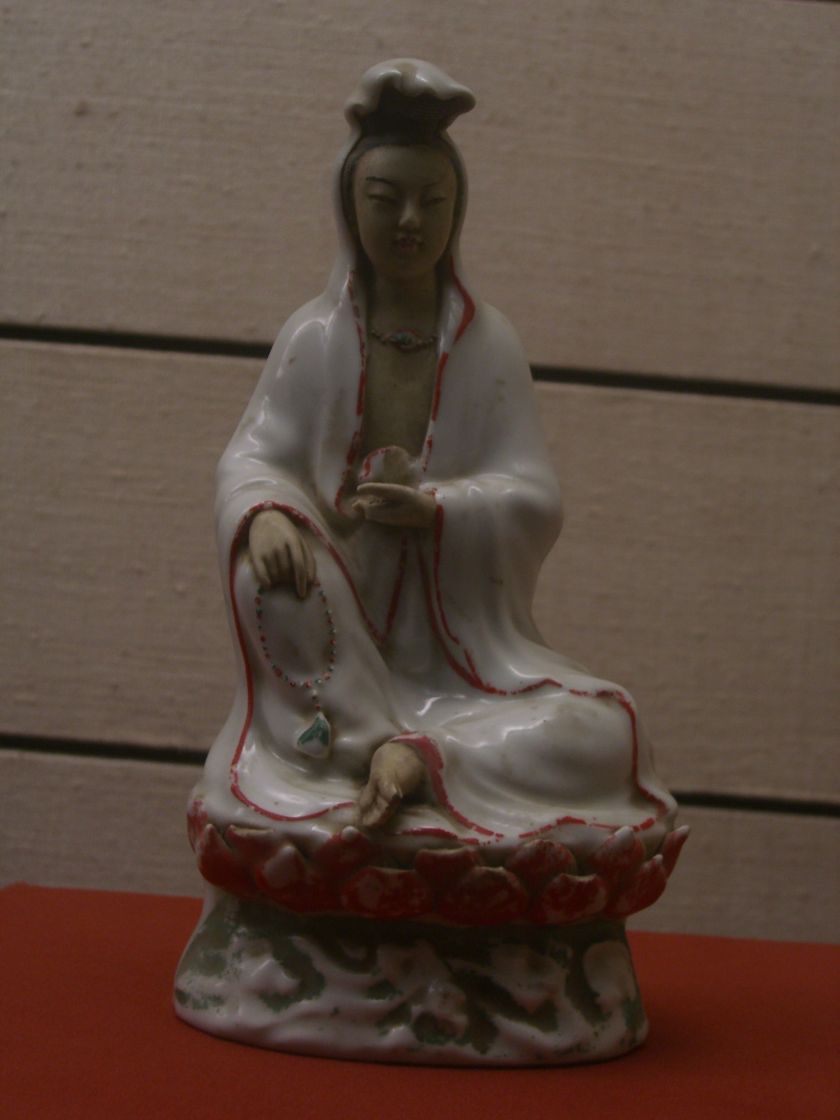
Guanyin has always been my favorite Bodhisattva. (Does anyone else have a favorite Bodhisattva?) Not sure whether it was the amazing 11th or 12th century “Guanyin of the Southern Sea” residing at the Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art in Kansas City or the Qing Dynasty Guanyin (Avalokitesvara) ceramic figure at the Shaanxi Historical Museum that made me fall in love with Guanyin. Having seen thousands of Guanyins in temples, museums, street markets, and antique shops throughout the world, these two are still my favorites. I loved that Guanyin was the God/Goddess of Compassion and that he/she could have been male or female in origin. The Lotus Sutra says that “Guanyin travels throughout the world guiding beings towards freedom from suffering.” The word, “Guanyin” in Chinese means “pays attention to all sounds” which may also be interpreted as “hearing all prayers and pleas for help.”
“There is no place where s/he will not manifest her/himself.
The suffering of those in troubled states of being;
Hell-dwellers, hungry ghosts and animals;
And the suffering of birth, old age, illness, and death
Will gradually be extinguished”
The Lotus Sutra, trans. Tsugunari Kubo and Akira Yuyama, Bukkyō Dendō Kyōkai 2007.
Guanyin, (Avalokiteshvara in India), was almost certainly a male figure when s/he first appeared in Chinese Buddhist temples during the early centuries of the Common Era. It wasn’t until the Song Dynasty (960-1279 CE) that Guanyin transmogrified fully into her current female form. The Ming Dynasty Buddhist, Miaoshan (妙善 miào shàn) is often portrayed as a human manifestation of Guanyin. Miaoshan was the youngest of three daughters. At an early age, she had wanted to be a follower of Buddha, but her father had other ideas and insisted that she marry. When she adamantly refused, her furious father punished her by sending her to a nunnery, which he later tried to burn down. Legend has it that he tried again to have his daughter killed. Two soldiers took Miaoshan out to an open space in the forest and drew their swords. But a tiger appeared and the soldiers dropped their swords and fled whereupon the tiger took Miaoshan to a cave on a mountain and left her there. Some time later, Miaoshan’s father became very sick. He was told that the only way he could be cured was by a compassionate person gouging out an eye and cutting off an arm. Miaoshan’s father did not believe that someone would actually step forward and make that kind of a sacrifice. In the end, it was Miaoshan who gouged out her eye and cut off an arm to cure him. When her father gazed upon his mutilated daughter, and realized that she was the compassionate person, he immediately realized what a selfish and heartless person he was, and begged her to forgive him. Some people believe that that thousand eyed, thousand armed Guanyin statues came into being as a result of the story about Miaoshan.
Guanyin statues and stories abound. One incarnation of the Guanyin statue which has always intrigued me is the one where she is carrying a baby (usually thought to be a baby boy.) I’ve often wondered whether that manifestation of Guanyin might have been influenced by Madonna statues brought in by Catholic priests when they first arrived China in the 14th century.
About 7 km (4.5 miles) due north of the Shaanxi History Museum, located in the heart of the old city of Xi’an, stands the best preserved and maintained city wall in all of China – with the possible exception of the wall around the Forbidden City in Beijing. Started in the Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE) and refurbished to its present state in the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644 CE), the total perimeter of the city wall is 13.7 km (8.5 miles). It is 15-18 meters (50-60 ‘) wide at the bottom and approximately 12-14 meters (40-45’) across on the top. The wall is approximately 12 meters (40 ‘) tall. Of the 6,000 cities in China which used to have walls, only about ten continue to exist today. A city within a city lies within these walls complete with schools, mosques, temples, commercial areas, museums, and anything else which makes up a city in China. One fun thing to do is to rent a bike on top of the wall. If you want, you can bike the entire perimeter of the wall.
One of my favorite places to visit within the wall is the Great Mosque. I actually lived in Xi’an for nearly a month in the early 2000’s. Every time I visited the mosque, it was quiet and serene. When I first went there in the early 80’s, I met a young English speaking Muslim student who lived and studied at the mosque. I wrote down his name and when I went back nearly twenty years later and asked about him, he was still there. I’m not sure he remembered me but we had a nice reunion .
The Muslim Quarter surrounding the Great Mosque has some of the best street food in Xi’an. A local Xi’an favorite is the Paomo Lamb & Pita Soup (羊肉泡馍 Yáng Roù Pào Mó). At its core, Paomo is a potage, a delicious thick broth filled with lamb and shredded flat bread. Dumplings are also nice in Xi’an. Unlike traditional jiaozi or xiaolongbao, dumplings here often contain spices like cumin, chives, and sweet garlic. Try the 灌汤饺子 Guàntāng Jiǎo which are translated as the Steamed Dumplings from Heaven.
You may remember Xuanzang (玄奘Xuán zàng) from the Monkey stories. He lived from 602-664 CE in the Tang Dynasty and was the real life Buddhist monk who took a pilgrimage to India to visit the sources of Buddhism in areas we now call India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Nepal. He was aware of an earlier Buddhist monk by the name of Fa Xian (法顯 Fǎxiǎn) who had traveled to India with nine other monks in the 5th century in a similar quest for Buddhist scriptures. It is said that the Big Wild Goose Pagoda (大雁塔 Dàyàn Tǎ) in Xi’an was the storage place of over 500 cases of Buddhist scriptures and artifacts that Xuanzang brought back to China from India – among them some of the most important of the Mahayana Buddhist scriptures.


 Samuel Bailey (sam.bailus@gmail.com) [CC BY (
Samuel Bailey (sam.bailus@gmail.com) [CC BY (
 Hiroki Ogawa [CC BY (
Hiroki Ogawa [CC BY ( Siim Sepp [CC BY-SA 3.0 (
Siim Sepp [CC BY-SA 3.0 (

